How to Backup MySQL Database to Filebase Using Bash
Filebase is a convenient and world's first object storage platform powered by multiple decentralized storage networks. Compared to traditional cloud providers, Filebase helps customers save over 90% on storage costs. It offers attractive pricing, a free 5 GB plan, and is easy to use once set up. Filebase has an S3 Compatible API that works out of the box with thousands of application SDKs, frameworks, and even data backup tools.
In this post, we will show you how to backup the MySQL database to Filebase using bash.
Table Of Contents
- Create a Bucket on Filebase
- Install S3cmd Tool
- Configure S3cmd to Connect Your Server to Filebase Bucket
- Use S3cmd to Backup MySQL Database to Filebase Bucket
- Conclusion
Create a Bucket on Filebase
First, you will need to create a bucket on Filebase where you want to store your MySQL databases. Follow the below steps to create a Filebase bucket.
Step 1 - First, sign in to your Filebase account.
Step 2 - Click on the Buckets in the left pane, you should see the following screen:

Step 3 - Click on the Create Bucket button. You should see the bucket creation screen:
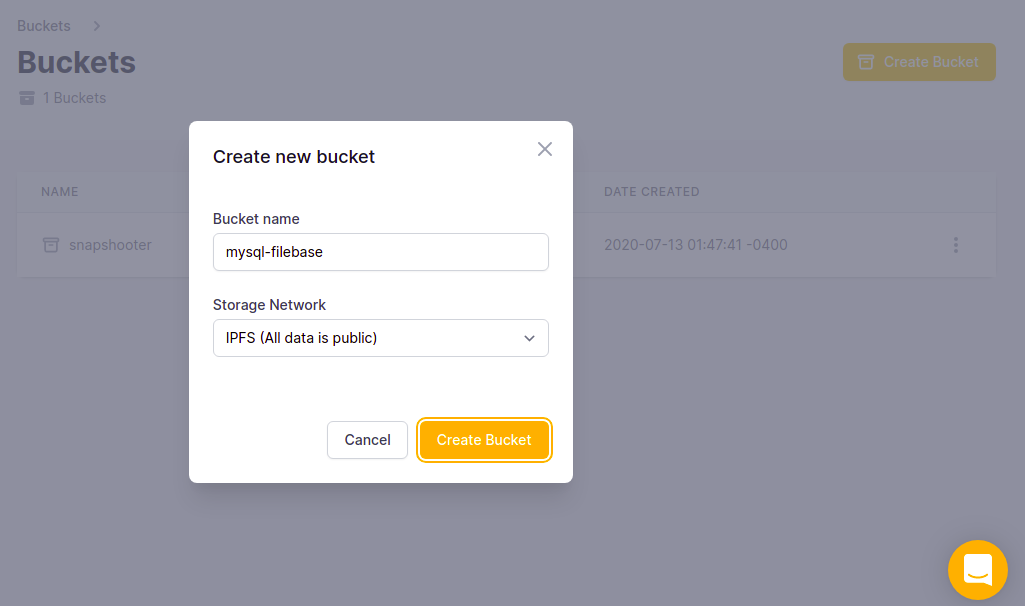
Step 4 - Provide your bucker name, choose your storage location, and click the Create Bucket button. Once the bucket is created, you should see the following screen:

Step 5 - Click on the Access Keys in the left pane, you should see your Filebase access key and secrets on the following screen:

Please note down this access key, secret key, and API endpoint. You will need all to connect to the Filebase bucket.
Install S3cmd Tool
Next, you will need to install the S3cmd tool on your MySQL database server from where you want to back up your MySQL database.
S3cmd is a free and open-source command-line tool that allows you to upload, download and manage data in Filebase bucket and other cloud storage service providers. Follow the below steps to install the S3cmd to your server.
First, log in to your server and install the Python and other dependencies by running the following command:
apt-get install python3 python3-setuptools curl -yNext, download the latest version of S3cmd using the following command:
curl -LO https://github.com/s3tools/s3cmd/releases/download/v2.2.0/s3cmd-2.2.0.tar.gzNext, extract the downloaded file with the following command:
tar -xvzf s3cmd-2.2.0.tar.gzNext, navigate to the extracted directory and install it using the following command:
cd s3cmd-2.2.0python3 setup.py installOnce the S3cmd is installed, verify the S3cmd version using the following command:
s3cmd --versionYou will get the following output:
s3cmd version 2.2.0Configure S3cmd to Connect Your Server to Filebase Bucket
Next, you will need to configure the S3cmd using the Filebase Access key and Secret key to connect the Filebase bucket.
Run the following command to configure s3cmd:
s3cmd --configureYou will be asked to provide your Filebase Access Key, Secret Key, Region, and Endpoint as shown below:
Enter new values or accept defaults in brackets with Enter.Refer to user manual for detailed description of all options. Access key and Secret key are your identifiers for Amazon S3. Leave them empty for using the env variables.Access Key: 54203D2S91DA6F043A3DSecret Key: JSo3sFt7vMF1v3iISArDwWvzSHsPlSsroaL1591ADefault Region [US]: us-east-1 Use "s3.amazonaws.com" for S3 Endpoint and not modify it to the target Amazon S3.S3 Endpoint [s3.amazonaws.com]: s3.filebase.com Use "%(bucket)s.s3.amazonaws.com" to the target Amazon S3. "%(bucket)s" and "%(location)s" vars can be usedif the target S3 system supports dns based buckets.DNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket [%(bucket)s.s3.amazonaws.com]: %(bucket)s.s3.filebase.com Encryption password is used to protect your files from readingby unauthorized persons while in transfer to S3Encryption password:Path to GPG program [/usr/bin/gpg]: When using secure HTTPS protocol all communication with Amazon S3servers is protected from 3rd party eavesdropping. This method isslower than plain HTTP, and can only be proxied with Python 2.7 or newerUse HTTPS protocol [Yes]: On some networks all internet access must go through a HTTP proxy.Try setting it here if you can't connect to S3 directlyHTTP Proxy server name: New settings: Access Key: 54203D2S91DA6F043A3D Secret Key: JSo3sFt7vMF1v3iISArDwWvzSHsPlSsroaL1591A Default Region: us-east-1 S3 Endpoint: s3.filebase.com DNS-style bucket+hostname:port template for accessing a bucket: %(bucket)s.s3.filebase.com Encryption password: Path to GPG program: /usr/bin/gpg Use HTTPS protocol: True HTTP Proxy server name: HTTP Proxy server port: 0 Test access with supplied credentials? [Y/n] YPlease wait, attempting to list all buckets...Success. Your access key and secret key worked fine :-) Now verifying that encryption works...Not configured. Never mind. Save settings? [y/N] yOnce the S3cmd is configured, you can verify your bucket information using the following command:
s3cmd info s3://mysql-filebase/You will get the following output:
s3://mysql-filebase/ (bucket): Location: us-east-1 Payer: none Expiration Rule: none Policy: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><ListBucketResult xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/"><Name>mysql-filebase</Name><Prefix/><Marker/><MaxKeys>1000</MaxKeys><IsTruncated>false</IsTruncated></ListBucketResult> CORS: none ACL: simon@snapshooter.io: FULL_CONTROLUse S3cmd to Backup MySQL Database to Filebase Bucket
S3cmd is now installed and configured to manage the Filebase bucket.
Next, log in to the server from where your MySQL server is hosted, then log in to the MySQL using the following command:
mysql -u root -pOnce you are logged in, list all MySQL databases using the following command:
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;+--------------------+| Database |+--------------------+| information_schema || mysql || performance_schema || sampledb |+--------------------+Now, exit from the MySQL shell using the following command:
mysql> EXIT;Next, create a backup of sampledb database using the following command:
mysqldump -u root -p sampledb > sampledb.sqlTo create a backup of all databases, run the following command:
mysqldump -u root -p --all-databases > alldb_backup.sqlNext, run the S3cmd command to copy the alldb_backup.sql backup file to the Filebase bucket:
s3cmd put alldb_backup.sql s3://mysql-filebase/You will get the following output:
upload: 'alldb_backup.sql' -> 's3://mysql-filebase/alldb_backup.sql' [part 1 of 2, 15MB] [1 of 1]15728640 of 15728640 100% in 0s 22.94 MB/s doneupload: 'alldb_backup.sql' -> 's3://mysql-filebase/alldb_backup.sql' [part 2 of 2, 5MB] [1 of 1]5242880 of 5242880 100% in 0s 15.37 MB/s doneTo copy sampledb.sql backup file to the Filebase bucket, run the following command:
s3cmd put sampledb.sql s3://mysql-filebase/You will get the following output:
upload: 'sampledb.sql' -> 's3://mysql-filebase/sampledb.sql' [1 of 1]2097152 of 2097152 100% in 0s 5.01 MB/s doneIf you want to back up the MySQL data directory to the Filebase bucket and compress it, run the following command:
tar -czvf - /var/lib/mysql/ | s3cmd put - s3://mysql-filebase/mysql_backup.tar.gzYou will get the following output:
upload: '<stdin>' -> 's3://mysql-filebase/mysql_backup.tar.gz' [part 1 of -, 679KB] [1 of 1]695429 of 695429 100% in 0s 5.08 MB/s doneYou can now verify all backups on the Filebase bucket using the following command:
s3cmd ls s3://mysql-filebaseYou will get the following output:
2022-07-15 05:16 20971520 s3://mysql-filebase/alldb_backup.sql2022-07-15 05:17 695429 s3://mysql-filebase/mysql_backup.tar.gz2022-07-15 05:17 2097152 s3://mysql-filebase/sampledb.sqlYou can also log in to the Filebase and verify your backup files as shown below:
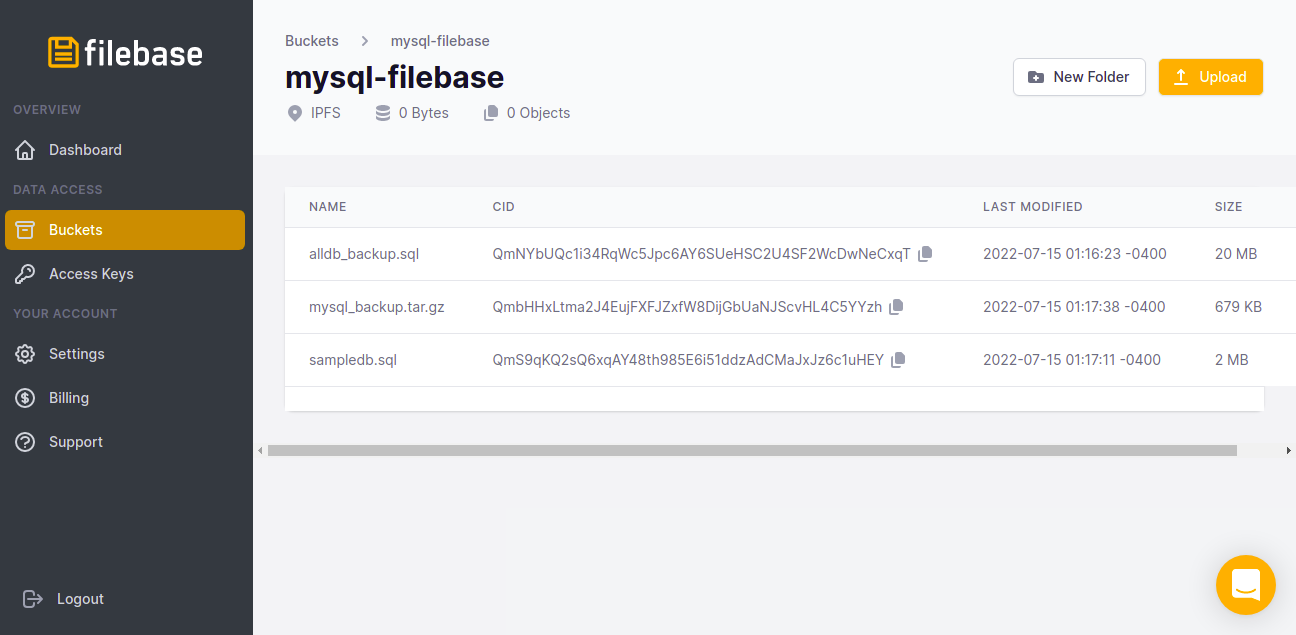
Conclusion
In this post, we showed you how to back up the MySQL database to Filebase using bash. You can now easily manage your Filebase bucket from your server using bash.
Scheduled MySQL Single Databases Backups SnapShooter
Backup a single MySQL database to your external storage
Learn more about MySQL Single Databases Backups
Get started for freeThank you for helping us improve!

